Mission Overview・Mission Flow
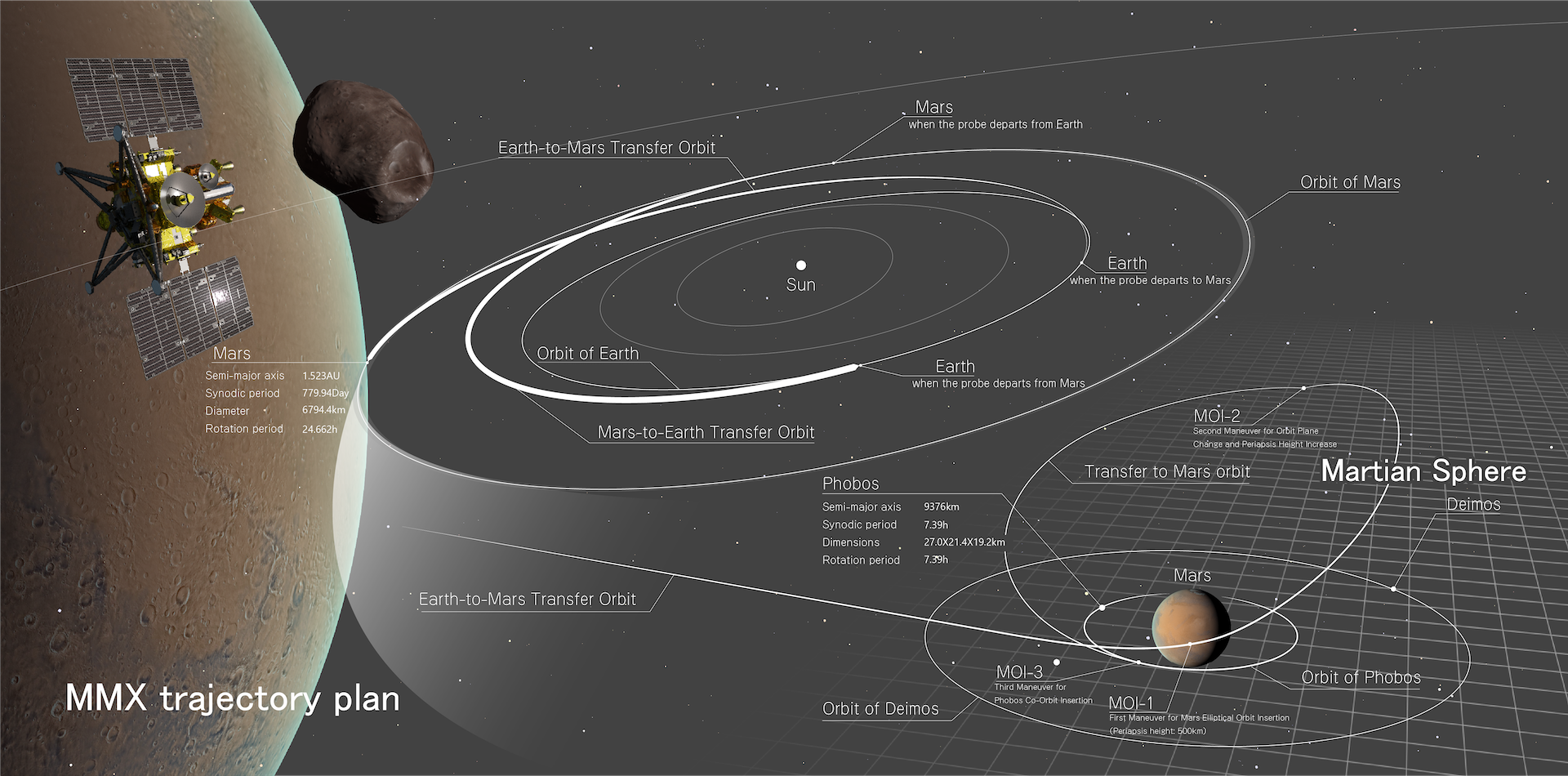
Mission Overview
MMX (Martian Moons eXploration) is a mission to explore the Martian moons.
Mars has two moons known as Phobos and Deimos. MMX is planning to collect surface material from Phobos and bring it back to the Earth (sample return). MMX is currently under development, with current plans to launch in fiscal year 2024
The image on the right shows a CG image of Phobos.

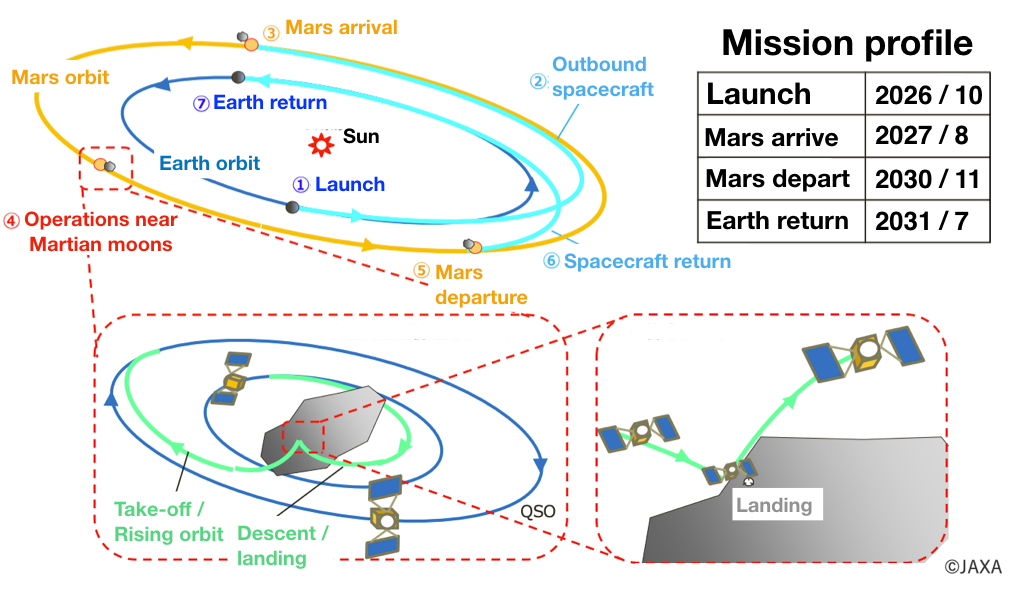
Mission Flow
About one year after launch, the MMX spacecraft will arrive at Mars. After that, MMX will enter an orbit (Quasi-Stationary Orbit: QSO) around the Martian moon, Phobos, and perform a series of observations. The period remaining in the vicinity of the Martian moon will be decided during on-going studies, such as observational planning. After observations and sample collection, MMX will return to the Earth after a journey of about one year and deliver the collected samples home.
Mission Objective
The MMX mission has the following objectives defined based on two different aspects: science and engineering.
Science
- Clarification of the origin of the Martian moons and the process of planet formation in the Solar System.
- Clarification of the evolution process of the Martian-sphere (Mars, Phobos, Deimos).
Engineering
- Establish the technology required for the return trip between the Earth and Mars.
- Establish advanced sampling techniques on celestial bodies.
- Establish optimal communication technologies using a newly developed ground station.
Expected Outcomes
There are two dominent theories as to the origin of the Martian moons: (A) the pair are asteroids captured after the formation of Mars or (B) the moons are fragments scattered during a giant collision (Giant Impact) with Mars that then coalesced. Based on the results of proximity observations and the analysis of collected samples, the most likely theory for the moons' formation can be clarified.
Through observations of Mars and its surrounding space from the vicinity of Martian moons, the mechanism for atmospheric material circulation and dissipation related to the Martian surface environment and climate change can be explored.
Together, these scientific investigations will allow MMX to contribute to the overall goal of "understanding the evolution of the pre-life environment as the condition that led to the birth and sustenance of the Solar System life environment" in the field of planetary science research.
